Geometry Quizzes
This angles quiz has Exercises with the following types of angles:
- Adjacent Angles - angles that share a common side and that have a common vertex
- Complementary Angles - angles that add together to make 90o
- Supplementary Angles - angles that add together to make 180o
- Opposite Angles - when two lines intersect they create two pairs of opposite angles. Opposite angles are equal.
- Acute Angles - angles that are less than 90o
- Right Angles - angles that are equal to 90o
- Obtuse Angles - angles that are more than 90o but less than 180o
Angles in Plane Geometry
Exercises with Bisectors, Medians and Altitudes
- The bisector of an angle is the line or line segment that divides the angle into two equal parts.
- The median of a triangle is a line segment that extends from one vertex of a triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side.
- An altitude is a segment from the vertex of a triangle to the opposite side that is perpendicular to that segment.
Bisectors, Medians and Altitudes Geometry Practice
Triangles Geometry Exercises
This quiz has exercises with right, scalene, obtuse, isosceles and equilateral triangles.
Some of the problems require knowledge of triangle similarity or congruence, the Pythagorean Theorem, understanding of altitudes, bisectors and medians.
Triangles Geometry Practice
Quadrilaterals Geometry Exercises
- Properties of different types of quadrilaterals: parallelogram, rhombus, trapezoid, rectangle, square
- Calculations of areas and perimeters of quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals Geometry Practice
Circles Geometry Exercises
- Properties of different types of quadrilaterals: parallelogram, rhombus, trapezoid, rectangle, square
- Calculations of areas, circumferences and arcs of circles
- Circles inscribed in triangles or quadrilaterals
- Circles circumscribed to triangles or quadrilaterals
Geometry Exercises with Circles
Areas Geometry Exercises
Exercises that use the following areas formulas:
- Square: A = a2, where a is the length of the side of the square.
- Rectangle: A = l×w, where l and w are the lengths of the rectangle's sides (length and width).
- Triangle: 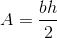 where b and h are the base and height
where b and h are the base and height
- Circle: A = πr2 where r is the radius.
- Trapezoid: 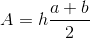 where a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides and the height of the trapezoid.
where a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides and the height of the trapezoid.
Geometry Practice with Areas of Geometric Figures
Pythagorean Theorem Geometry Exercises
The Pythagorean Theorem states that for a right triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c,
c2 = a2 + b2
The Cosine Law is a generalization of the Pythagorean Theorem. For a triangle with sides a, b, and c and angle C opposite the side c,
Pythagorean Theorem Geometry Quiz
Equations in Geometry Exercises
- Equations of lines, slope, x-intercept and y-intercept
- Points of intersection of lines, parallel lines, perpendicular lines in the Cartesian coordinate system
- Equations of circles, coordinates of the center of a circle
- Points of intersection between lines and circles, lines tangent to circles
Equations of Geometric Figures
Exercises with Trigonometric Identities
- Exercises with the unit circle, definition of sine, cosine, and tangent
- Exercises with trigonometric equations and identities
- Trigonometry with right triangles
Trigonometric Identities Quiz
Modeling Geometry Exercises
Modeling with geometry problems tests students in the following critical areas:
- application of geometric concepts in modeling situations
- use of geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects
- application of concepts of density based on area and volume in modeling situations
Modeling Geometry Exercises
Other Geometry Resources
GeoGebra visualization tools for geometry